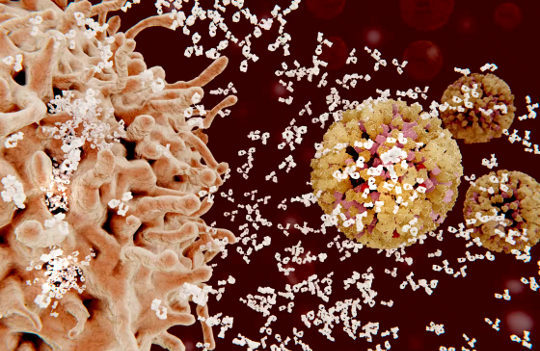
Inflammation is a process in which antibody-producing cells – like the large beige cell on the left of this image – rush to the site of an infection to attack an invader, such as the flu virus in yellow. Juan Gaertner/Science Photo Library via Getty Images
When your body fights off an infection, you develop a fever. If you have arthritis, your joints will hurt. If a bee stings your hand, your hand will swell up and become stiff. These are all manifestations of inflammation occurring in the body.
We are two immunologists who study how the immune system reacts during infections, vaccination and autoimmune diseases where the body starts attacking itself.
While inflammation is commonly associated with the pain of an injury or the many diseases it can cause, it is an important part of the normal immune response. The problems arise when this normally helpful function overreacts or overstays its welcome.
What is inflammation?
Generally speaking, the term inflammation refers to all activities of the immune system that occur where the body is trying to fight off potential or real infections, clear toxic molecules or recover from physical injury. There are five classic physical signs of acute inflammation: heat, pain, redness, swelling and loss of function. Low-grade inflammation might not even produce noticeable symptoms, but the underlying cellular process is the same.
Get The Latest By Email
Take a bee sting, for example. The immune system is like a military unit with a wide range of tools in its arsenal. After sensing the toxins, bacteria and physical damage from the sting, the immune system deploys various types of immune cells to the site of the sting. These include T cells, B cells, macrophages and neutrophils, among other cells.
The B cells produce antibodies. Those antibodies can kill any bacteria in the wound and neutralize toxins from the sting. Macrophages and neutrophils engulf bacteria and destroy them. T cells don’t produce antibodies, but kill any virus-infected cell to prevent viral spread.
Additionally, these immune cells produce hundreds of types of molecules called cytokines – otherwise known as mediators – that help fight threats and repair harm to the body. But just like in a military attack, inflammation comes with collateral damage.
The mediators that help kill bacteria also kill some healthy cells. Other similar mediating molecules cause blood vessels to leak, leading to accumulation of fluid and influx of more immune cells.
This collateral damage is the reason you develop swelling, redness and pain around a bee sting or after getting a flu shot. Once the immune system clears an infection or foreign invader – whether the toxin in a bee sting or a chemical from the environment – different parts of the inflammatory response take over and help repair the damaged tissue.
After a few days, your body will neutralize the poison from the sting, eliminate any bacteria that got inside and heal any tissue that was harmed
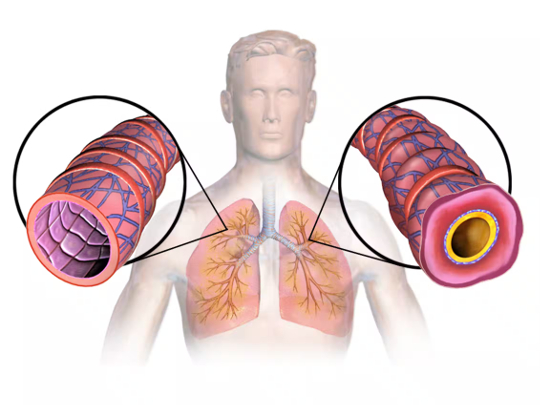
Asthma is caused by inflammation that leads to swelling and a narrowing of airways in the lungs, as seen in the right cutaway in this image. BruceBlaus/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Inflammation as a cause of disease
Inflammation is a double-edged sword. It is critical for fighting infections and repairing damaged tissue, but when inflammation occurs for the wrong reasons or becomes chronic, the damage it causes can be harmful.
Allergies, for example, develop when the immune system mistakenly recognizes innocuous substances – like peanuts or pollen – as dangerous. The harm can be minor, like itchy skin, or dangerous if someone’s throat closes up.
Chronic inflammation damages tissues over time and can lead to many noninfectious clinical disorders, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, obesity, diabetes and some types of cancers.
The immune system can sometimes mistake one’s own organs and tissues for invaders, leading to inflammation throughout the body or in specific areas. This self-targeted inflammation is what causes the symptoms of autoimmune diseases such as lupus and arthritis.
Another cause of chronic inflammation that researchers like us are currently studying is defects in the mechanisms that curtail inflammation after the body clears an infection.
While inflammation mostly plays out at a cellular level in the body, it is far from a simple mechanism that happens in isolation. Stress, diet and nutrition, as well as genetic and environmental factors, have all been shown to regulate inflammation in some way.
There is still a lot to be learned about what leads to harmful forms of inflammation, but a healthy diet and avoiding stress can go a long way toward helping maintain the delicate balance between a strong immune response and harmful chronic inflammation.![]()
About The Author
Prakash Nagarkatti, Professor of Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology, University of South Carolina and Mitzi Nagarkatti, Professor of Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology, University of South Carolina
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
books_health







